Navigating the bidding process can be a daunting yet crucial task for businesses aiming to secure new contracts and opportunities. Whether it’s a small local project or a large government contract, understanding the intricacies of bidding helps companies stand out in a competitive market. This process not only involves submitting a proposal but also requires a deep understanding of market trends, pricing strategies, and client needs.
Bidding Process
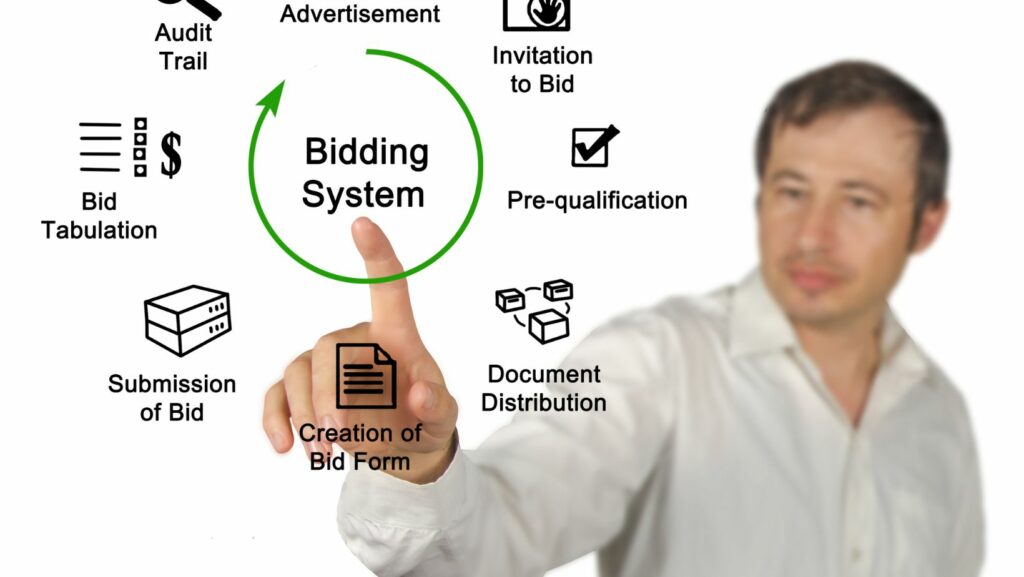
 The bidding process is paramount for businesses eager to secure new contracts and expand opportunities. This section delves deeper into the critical aspects of the bidding system.
The bidding process is paramount for businesses eager to secure new contracts and expand opportunities. This section delves deeper into the critical aspects of the bidding system.
Bidding refers to a competitive method where various entities, such as companies or contractors, propose their offers in hopes of acquiring a project or job. It’s a systematic approach used primarily in industries that deal with large-scale projects, services, or procurement of goods. The primary goal is to select the most suitable proposal that meets the project’s requirements while offering the best value.
Types of Bidding
There are several distinct types of bidding, each catering to different project needs and industry standards. These include:
-
Open Bidding: Open to all interested bidders, providing transparency and equal opportunity. Examples include government contracts and public construction projects.
-
Closed Bidding: Invitations are extended to a select group of bidders, often used when requiring specialized skills or when confidentiality is a concern.
-
Online Bidding: Utilized increasingly in the digital age, allowing companies to submit bids through online platforms. This method is common in IT and creative sectors.
Key Elements of a Successful Bidding Process
In a successful bidding process, the preparation of bid documents and the management of bid submission and opening are pivotal. These phases ensure clarity, compliance, and competitive fairness in acquiring contracts.
Preparation of Bid Documents
 Preparing bid documents requires meticulous attention to detail. Businesses must include all necessary information that defines the project scope, timelines, and terms. The documents usually comprise the bidding form, project blueprints, terms and conditions, and any supplementary information. Companies must align their bids with the client’s requirements, which enhances their likelihood of winning if they’ll offer better value propositions than competitors. It’s crucial to avoid over or under-quoting which can result from inaccurate data analysis or misinterpretation of the project scope. Moreover, incorporating clear, concise language and organized documentation helps eliminate ambiguities and mitigates risks of non-compliance, thus boosting the firm’s credibility and appeal.
Preparing bid documents requires meticulous attention to detail. Businesses must include all necessary information that defines the project scope, timelines, and terms. The documents usually comprise the bidding form, project blueprints, terms and conditions, and any supplementary information. Companies must align their bids with the client’s requirements, which enhances their likelihood of winning if they’ll offer better value propositions than competitors. It’s crucial to avoid over or under-quoting which can result from inaccurate data analysis or misinterpretation of the project scope. Moreover, incorporating clear, concise language and organized documentation helps eliminate ambiguities and mitigates risks of non-compliance, thus boosting the firm’s credibility and appeal.
Submission and Opening of Bids
The bid submission phase is characterized by adherence to deadlines and procedural guidelines. Businesses submit their bids within a specified timeframe usually outlined in the bid documents. Once the deadline occurs, the bid opening process begins—often publicly—to maintain transparency. This stage is critical as it marks the point where all received documents are analyzed for adherence to the set guidelines and qualifications stated in the bid request. Organizers ensure that all bids are treated equitably, preventing any form of bias or malpractice.
Common Challenges in the Bidding Process
The bidding process can present a range of challenges that can hinder a business’s ability to secure contracts. Navigating these obstacles is crucial for maintaining competitiveness and achieving success.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
 Navigating legal and regulatory challenges requires a deep understanding of the specific laws and guidelines that govern bidding activities. Businesses often encounter complexities related to compliance with local, national, and international regulations. For instance, companies must ensure their bids conform to anti-corruption laws, environmental standards, and labor regulations, which vary widely by jurisdiction. Failure to comply can lead to disqualification from the bidding process, legal penalties, and damage to reputation. Certifications and licenses specific to particular industries also play a critical role, necessitating thorough verification and updates to align with current legal standards.
Navigating legal and regulatory challenges requires a deep understanding of the specific laws and guidelines that govern bidding activities. Businesses often encounter complexities related to compliance with local, national, and international regulations. For instance, companies must ensure their bids conform to anti-corruption laws, environmental standards, and labor regulations, which vary widely by jurisdiction. Failure to comply can lead to disqualification from the bidding process, legal penalties, and damage to reputation. Certifications and licenses specific to particular industries also play a critical role, necessitating thorough verification and updates to align with current legal standards.
Technical and Financial Assessment Issues
Addressing technical and financial assessment issues is pivotal for ensuring bid accuracy and viability. Bidders frequently face difficulties in accurately estimating costs and timelines, especially for large and complex projects. Misjudgments can lead to bids that are either too high, risking non-selection, or too low, resulting in financial losses. Technical assessments require precise understanding of project specifications and the ability to evaluate technological feasibility, resource availability, and potential risks. Financial assessments involve rigorous scrutiny of budget estimates, funding sources, and financial stability.